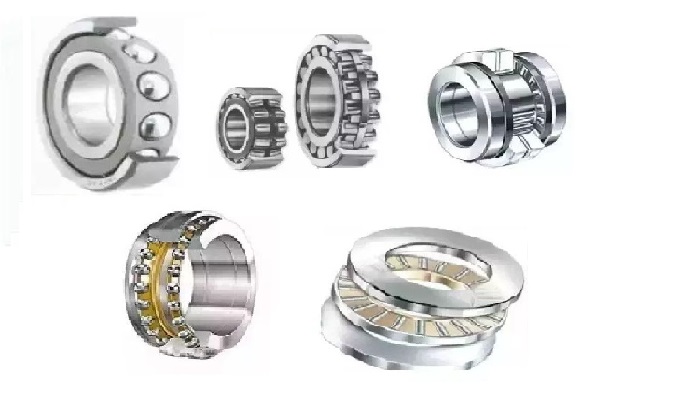
I. Bearing Selection & Performance
1. What type of bearing housing is suitable for high-load conditions?
Double-bearing housings are recommended for heavy-load environments to ensure stability for rotating shafts and transmission components.
2. How does stainless steel bearing performance compare to standard bearing steel?
Stainless steel bearings (e.g., SUS420/SUS440C) have hardness, speed, and load capacities close to bearing steel. SUS304/SUS316 are softer and suitable only for low-speed, low-load applications.
3. Is the SUS-BDR series waterproof?
No. Though made of rust-resistant stainless steel, prolonged water immersion can still cause corrosion.
4. Are stainless steel bearings completely rust-proof?
While highly corrosion-resistant, they may rust under extreme conditions. Performance depends on material composition and environmental exposure.
5. Why do bearings rust? How to prevent it?
Bearing steel contains limited chromium (Cr), insufficient for full rust prevention. To mitigate rust:
•Use stainless steel for exposed environments.
•Maintain dryness, avoid liquid contact, apply anti-rust coatings.
•Store in vacuum packaging and control humidity.
II. Installation & Assembly
6. Bearing housing installation precautions:
Install the housing first, then the shaft. Ensure mounting surfaces are flat and rigid to prolong bearing life.
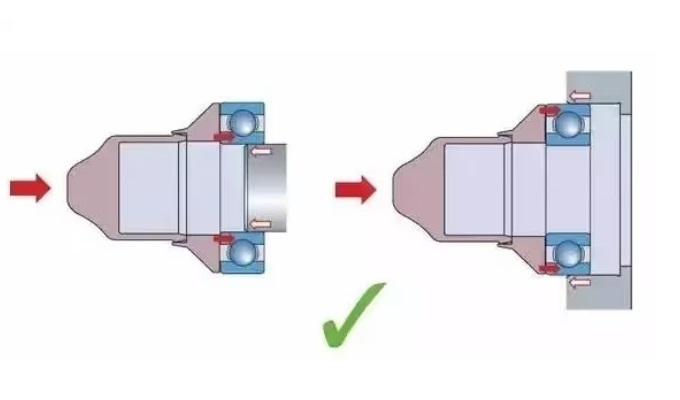
7. Why does a single-row angular contact bearing disassemble during installation?
These bearings withstand axial load in one direction only. Incorrect installation orientation leads to failure.
8. Bearing installation methods:
•Clearance fit: Press-fit installation.
•Transition fit: Use sleeve installation.
•Interference fit: Apply heating/cooling methods.
9. DB vs. DF pairing: Which is better?
•Back-to-back (DB): Wider end faces face each other, enhancing radial/axial rigidity and deformation resistance.
•Face-to-face (DF): Narrower end faces face each other, allowing higher preload but lower rigidity.
III. Shaft & Tolerance
10. Recommended shaft tolerance for bearing housings:
Use shafts with g6 tolerance.
11. Can casting housing dimensions serve as locating references?
No. Cast housings have CT9 tolerance (large variation), unsuitable for precision positioning.
IV. Fit Types
12. Difference between transition fit and clearance fit:
•Transition fit: Tight fit between bearing core and housing; alignment requires torque adjustment via the shaft.
•Clearance fit: Loose fit for easier alignment.
V. Maintenance & Lubrication
13. Do bearings require lubrication?
•BBK series (oil-free): Lubricant must be added manually.
•Open/single-shielded bearings: Lubricate before use and maintain periodically.
VI. Troubleshooting
14. Axial play after shaft-housing assembly:
Secure bearings axially with retaining rings or nuts, avoiding interference with C-clips.