I. Definition
Pin:
1. Locating Pin: A component used to establish a reference point for positioning a workpiece, either by using a hole in the workpiece or in combination with a bushing. It is a common locating element that ensures the correct relative positioning of parts, playing a key role in positioning and securing workpieces during manufacturing and assembly.
2. Connecting Pin: Utilized for connecting a shaft to a hub or other components and capable of transmitting small loads.
Bushings are used in combination with locating pins to provide a guiding function. The hardness of the bushing is slightly lower than that of the locating pin, effectively protecting the pin from rapid wear and maintaining locating precision. Bushings are easy to replace once worn out, protecting the baseplate or workpiece from damage.
II. Characteristics
1. High Precision on Working Surfaces
High Locating Precision: The working surfaces of pins and bushings undergo precision machining, ensuring high locating accuracy during use, which is crucial for the correct assembly and operation of mechanical parts.
Good Surface Finish: Precision machining ensures a smooth surface, reducing friction and extending the life of the parts.
2. Adequate Strength and Rigidity
Material Selection: Pins and bushings are typically made from high-strength alloy steel or other durable materials to prevent deformation or breakage under external forces.
Structural Design: Designed to withstand various stresses in the working environment, ensuring stability and reliability under high load or impact conditions.
3. High Wear Resistance
Surface Treatment: Pins and bushings often undergo surface treatments such as quenching, carburizing, or chrome plating to enhance wear resistance, significantly improving hardness and durability.
Self-Lubricating Materials: Some advanced bushing materials have self-lubricating properties, reducing friction and wear, thereby extending their service life.
4. Good Machinability (Processing/Assembly/Replacement)
Machinability: Designed for easy machining with standardized dimensions and shapes, facilitating mass production and quality control.
Convenient Assembly: Easy to install and remove, usually without requiring complex tools or equipment, significantly improving production and maintenance efficiency.
Replaceability: Bushings are designed to be easily replaceable, when worn, they can be quickly replaced to protect other critical components from damage.
5. Diverse Structural and Functional Selection
Variety of Specifications: Available in various sizes and specifications to meet different mechanical equipment and working conditions.
Functional Design: Depending on the application, pins and bushings can be designed as different functional types such as fixed pins, movable pins, and guiding pins to meet various mechanical needs.
Customized Services: Manufacturers can provide customized pins and bushings for specific technical requirements and application environments.
III. Products Types and Shapes
Pins:
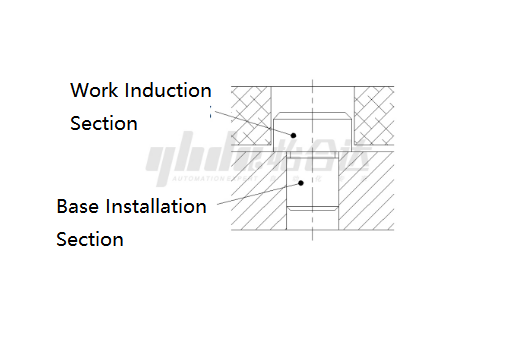
Pins are described based on their ends, each playing a role in positioning and connecting. The installation end is for installation and securing, usually not frequently removed, while the workpiece end is for positioning and transmitting relative movement, often requiring frequent "insertion" and "removal." The workpiece end is crucial for the pin's longevity and precision.
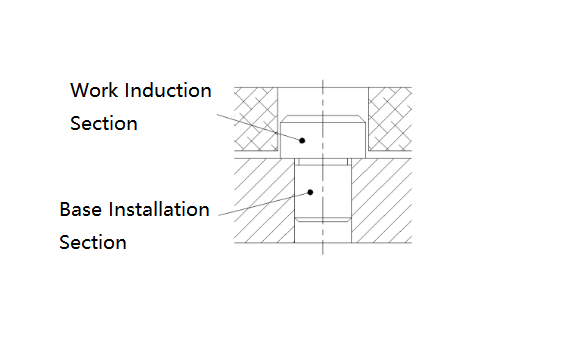
1. Workpiece End:
① Head Size: Large head, small head
② Head Section: Round head, multi-faceted head (diamond/triangular)
③ Head Shape: Straight rod, tapered, arc-shaped, spherical, flat head, with shoulder
2. Base Installation Part: Press-fit, internal thread, external thread, ring groove, slotted
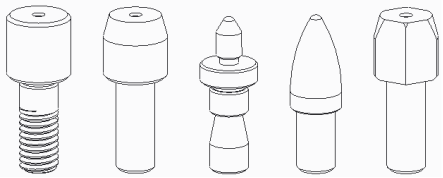
3. Function and Use: Standard pin, hinge pin, cantilever pin, step bolt, rolling pin, jig locating pin
Bushings:
1. Connection Type: Standard, with shoulder, flange, anti-fall (ring groove/slotted)
2. Structural Features: Thin-walled, elongated hole, self-lubricating, copper alloy
IV. Quick Selection Criteria for Locating Pins and Bushings
1. Choose appropriate size tolerances and precision requirements based on the working conditions.
2. For high rust resistance requirements, consider SUS304 stainless steel and surface-treated products, surface treatments for rust resistance: hard chrome/nickel plating > black oxide > untreated.
3. Custom non-standard sizes are accepted based on provided drawings.
Step 1: Confirm the Structure and Types of Locating Pins and Bushings
| Type | |||
| Locating pin | Straight type locating pin | Bushing | Shoulderless bushings |
| Step type locating pin | Shoulder bushings | ||
| Long-shoulder type locating pin | Flange bushings | ||
| Automobile welding locating pin | Special-shaped hole bushings | ||
| Ceramic locating pin | Bushings for ceramic locating pins | ||
| High hardness stainless steel locating pin | High-hardness stainless steel bushings | ||
| ... | ... | ||
Product Display:

Step 2: Installation Methods
Common installation methods: press-fit, internal thread, external thread. Fixing methods: press-fit, nut fixation, screw fixation.
Step 3: Material and Treatment Selection
Common Material:
| Material | Quenching hardness | Surface treatment |
| SKS3 | 53~ 58HRC | - |
| 53 ~ 58HRC, coating hardness 850HV | Hard chrome plating, coating thickness 3~5um | |
| 58~ 61HRC | - | |
| 58~ 61HRC, coating hardness 850HV | Hard chrome plating, coating thickness 3~5um | |
| SKS93 | 54 ~ 58HRC | - |
| Blackened | ||
| Electroless nickel plating | ||
| 56~ 60HRC | - | |
| Electroless Nickel Plating | ||
| SKD11 | 53~ 58HRC | - |
| 53 ~ 58HRC, coating hardness 850HV | Hard chrome plating, coating thickness 3~5um | |
| SUJ2 | 50~ 55HRC | - |
| Blackened | ||
| Electroless nickel plating | ||
| HRC56~, coating hardness 850HV | Hard chrome plating, coating thickness 3~5um | |
| SUS304 | - | - |
| Coating hardness 850HV ~ | Hard chrome plating, coating thickness 3~5um | |
| SUS440C | 48~ 53HRC | - |
| S45C | 43~ 48HRC | - |
| 43~ 48HRC | Blackened | |
| 43 ~ 48HRC, coating hardness 850HV | Hard chrome plating, coating thickness 3~5um | |
| ... | ... | ... |
Non-metal materials:
| Material | Usage Environment |
| Polyoxymethylene | -45~95°C |
| Polyacetal | -45~95°C |
| MC nylon | -40~120°C |
| Conductive MC nylon CDR2 | -40~120°C |
| PEEK | -50~200°C |
| Zirconium oxide | High hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, insulation |
| Aluminum oxide 995 | |
| ... | ... |
Step 4: Size and Tolerance Selection
Locating pins and bushings are categorized as fixed or adjustable. Fixed sizes are selected from available options, while adjustable sizes can be specified within a range. The smallest pin diameter can be 0.4mm, bushing wall thickness can be 1mm, surface roughness can reach Ra0.4, tolerance grade IT6, diameter tolerance within 5μm, length tolerance can reach 0.01mm.
Step 5: Additional Processing Options
Non-standard customizations are provided based on specific application needs.
Ⅴ. Definition and Explanation
Form and position tolerances, also known as geometric tolerances, include shape and position tolerances, indicating permissible variations in geometry.
- Shape Tolerances: Allowable variation in a single actual feature’s shape, including straightness, flatness, roundness, cylindricity, line profile, and surface profile.
- Position Tolerances: Allowable variation in the relative position of associated features to a reference, including parallelism, perpendicularity, angularity, coaxiality, symmetry, position, circular runout, and total runout.
Form and Position Tolerances for Locating Pins and Bushings:
Considering factors such as machining errors, tool movement errors, deformation due to clamping force and cutting force, and internal stress release, various shape and position errors may occur. To ensure proper function, appropriate form and position tolerances must be specified.
Key form and position tolerances for pins and bushings include:
- Coaxiality: Ensures the measured axis aligns with the reference axis, maintaining alignment accuracy for proper positioning and fit.
- Perpendicularity: Ensures features maintain a 90° angle relative to a reference, crucial for accurate positioning and wear prevention.
- Parallelism: Ensures measured elements maintain equidistant alignment with the reference, essential for smooth insertion and accurate positioning.
- Symmetry: Ensures symmetrical features maintain alignment with a central plane, critical for certain types of bushings.
Selection of Form and Position Tolerances:
Form and position tolerances should be specified according to different working conditions and application scenarios.
VI. Common Installation and Removal Methods
Pins and bushings are typically installed and removed using three common methods: press-fit, nut fixation, and screw fixation.
1. Press-Fit:
Precautions:
During installation, the locating pin and bushing should be pressed in horizontally, and avoid installation in an inclined state to prevent the locating pin, bushing and mounting hole from being damaged, deformed or stuck.
2. Nut Fixation:

Precautions:
According to different scenarios, choose suitable spring washers or anti-loosening nuts to prevent loosening, according to the material of the clamp, choose gaskets to prevent deformation and wear of the clamp body.
Locking pins of different materials have different thread strengths, and the appropriate tightening torque needs to be used to tighten the threads.
The use of spring washers, washers, anti-loosening nuts, and anti-loosening agents will also affect the choice of tightening torque. It is generally not recommended to directly screw the external thread locating pin with the threaded hole of the clamp body. The reason is that the machining accuracy of the threaded hole of the clamp body is insufficient, and the installation accuracy of the locating pin cannot be guaranteed, which affects the use effect.
3. Screw Fixation:

Precautions:
The same standard screws should be used to tighten the positioning pin to avoid different pitches and failure to tighten, if the working conditions are often subject to vibration, it is recommended to add spring washers for anti-loosening when tightening to prevent the positioning pin and bushing from loosening during use.
VII. Usage and Maintenance
Proper usage and maintenance are crucial for extending the lifespan of locating pins and bushings. Consider the following:
1. Rust Prevention:
When choosing a product, you need to consider the application. If there is a requirement for rust prevention, give priority to SUS304 stainless steel or products with rust prevention treatment on the surface. Material rust prevention ability: SUS304>SUS440C>SKS3/40Cr/45 steel, Surface treatment rust prevention ability: hard chrome plating/nickel plating>blackening>products without surface treatment. In addition to choosing the right product, during use, spraying rust prevention oil regularly and maintaining a low temperature and low humidity working and storage environment will greatly increase the service life of the product.
2. Technical Requirements for Workpiece Holes:
For the product itself, ensuring the dimensional accuracy and surface roughness of the locating pin and bushing mounting holes can extend the product life and reduce the number of subsequent replacements and maintenance. For the workpiece mounting holes, ensuring the dimensional accuracy and surface roughness can avoid mismatching and damage to the workpiece during installation.
3. Installation Requirements for External Thread Products:
Refer to the strength grade of the bolt to select a reasonable initial tightening force. If the threaded part is in an overload state for a long time, the product life will be shortened and even overload fracture may occur.
The following table is a recommended tightening torque table:
| Recommended tightening torque for external thread (N·m) | |||
| Thread specification | Strength classification | ||
| 8.8 | 10.9 | 12.9 | |
| Carbon steel/Alloy steel | 35CrM0/40Cr | 35CrM0/40Cr | |
| HRC20-30 | HRC30-35 | HRC35-40 | |
| M3 | 0.8~1.0 | 1.2~1.5 | 1.5~1.8 |
| M4 | 2.0~2.5 | 3.0~3.5 | 3.5~4.0 |
| M5 | 4.0~4.5 | 6.5~7.0 | 7.5~8.0 |
| M6 | 7.5~8.0 | 11.0~11.8 | 13.0~13.8 |
| M8 | 19.0~19.5 | 28.0~28.6 | 33.0~33.5 |
| M10 | 30~38 | 50~58 | 60~~68 |
| M12 | 60~68 | 90~98 | 110~116 |
| M16 | 140~167 | 220~246 | 260~287 |
| M20 | 300~336 | 450~479 | 530~560 |
| *The data in the table are experimental test data, non-standard values, and are for reference only. | |||
4. Installation Requirements for Standard Types:
The standard installation part and the workpiece are interference/transition fit, and external force is required for installation. Please keep the force direction parallel to the installation hole during installation. Do not knock sideways to install, otherwise there will be a risk of breakage. When installing products made of easily deformable materials, you need to use specific material tools (such as: copper hammer, non-metallic hammer head, etc.) to avoid deformation and damage of the product, which will affect its use.
VIII. Application Examples
Industry Applications:
Medical, semiconductor, lithium battery, electronics, smartphones, robotics, machine tools, precision molds, and automotive automation equipment.
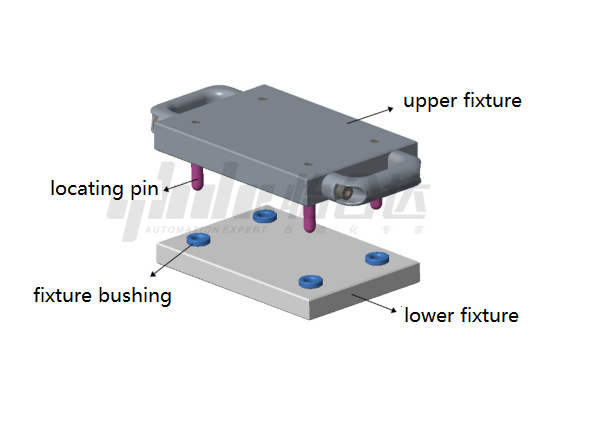
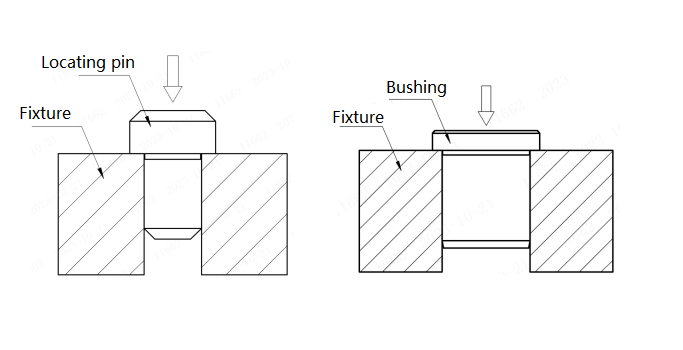
Application Example of Locating Pins and Bushings:
Shown is a fixture setup for machining, where the combination of locating pins and bushings ensures precise repetitive positioning of workpieces on a machine. The internal diameter tolerance of the fixture bushing is G6, ensuring H7 after press-fit installation. Locating pins undergo quenching, grinding, and hard chrome plating, significantly enhancing wear resistance and precision stability, thereby extending product life.